EMBP Therapy Administration
Our Electromagnetic Brain Pulse (EMBP™) therapy is a revolutionary neural modulation treatment designed to restore brain functionality and address various cognitive challenges.
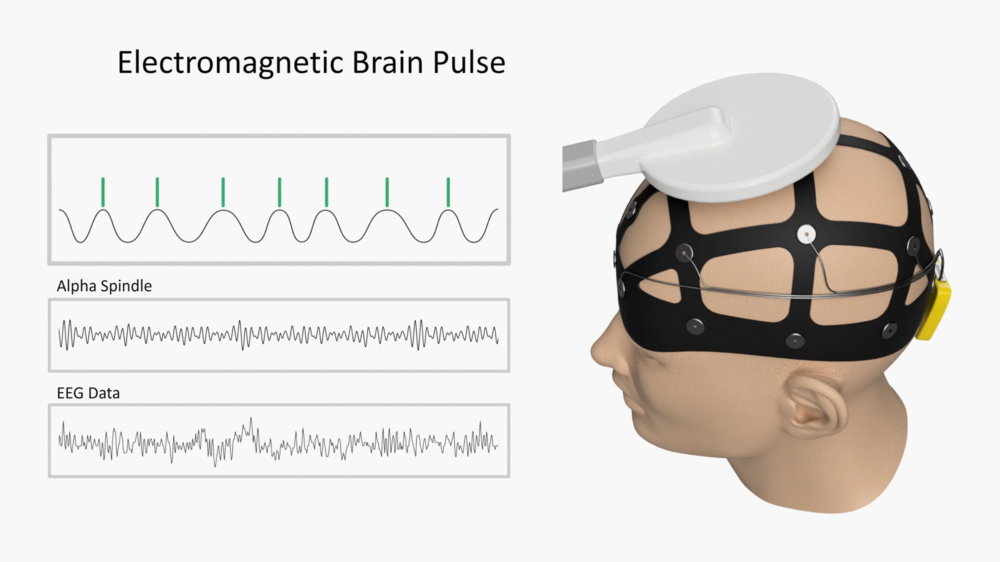
ELECTROMAGNETIC BRAIN PULSE (EMBP™)
is a revolutionary neural modulation therapy designed to restore brain functionality and combat various cognitive challenges. EMBP therapy offers a non-invasive approach to enhancing brain health, effectively addressing conditions such as addiction, depression, anxiety, lack of focus, and metabolic disorders that contribute to chronic illnesses.
Benefits
- Promotes brain recovery and combats cognitive decline.
- Enhances mental resilience and overall brain health.
- Tailored to address specific cognitive issues.
Customer Support
24 Hour Ready
support@energyguidedbrain.com
(555) 987-6543
Book Appointment
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
How it works
The primary objective of treatment is durable, functional recovery depending upon the presenting signs and symptoms. Commonly reported benefits may include:
- Reduction of symptom severity,
- Improvement in quality of sleep,
- Improvement in sleep duration,
- Reduction in anxiety,
- Reduction in VAS Pain Scores,
- Reduction and elimination of opioid use,
- Reduction and elimination of alcohol use,
- Improvement in concentration and focus,
- Improvement in mood,
- Improvement in attention span,
- Improvement in sociability,
- Improvement in motivation,
- Improvement in clarity of thought,
- Reduction in cravings (e.g. drugs and alcohol),
- Improvement in emotional stability,
- Improvement in ability to adapt to change,
- Improvement in self-confidence and self-esteem,
- Improvement in resiliency, and
- Re-discovery of sense of humor.


